Types of Polymer
TRP Polymer Solutions offers the following types of polymers, which are specially formulated to meet your specifications regarding hardness, tensile strength, elongation at break, compression set and specific colours. For further information, please contact one of our technical experts today and we will be pleased to offer advice and guidance on the most effective polymeric material for your application.
Why choose TRP Polymer Solutions?
At TRP Polymer Solutions, we make it our goal to solve your most challenging problems. Whether you require the development of a brand-new product, or the overhaul of an existing one, we will work closely with you at every step of the process to develop an optimal sealing solution. That begins with choosing the right polymeric material, and at TRP Polymer Solutions we have a range of high performance materials to choose from.
The various types of polymers that we employ range from those that are suitable for extreme weathering and are flame retardant (Polyurethane), through to polymers that are made for low temperatures or are steam resistant (FKM, also referred to as Fluoroelastomer type 1). No matter what polymer you require, TRP Polymer Solutions has the optimal material to fit your application requirements.
Our range of polymeric materials
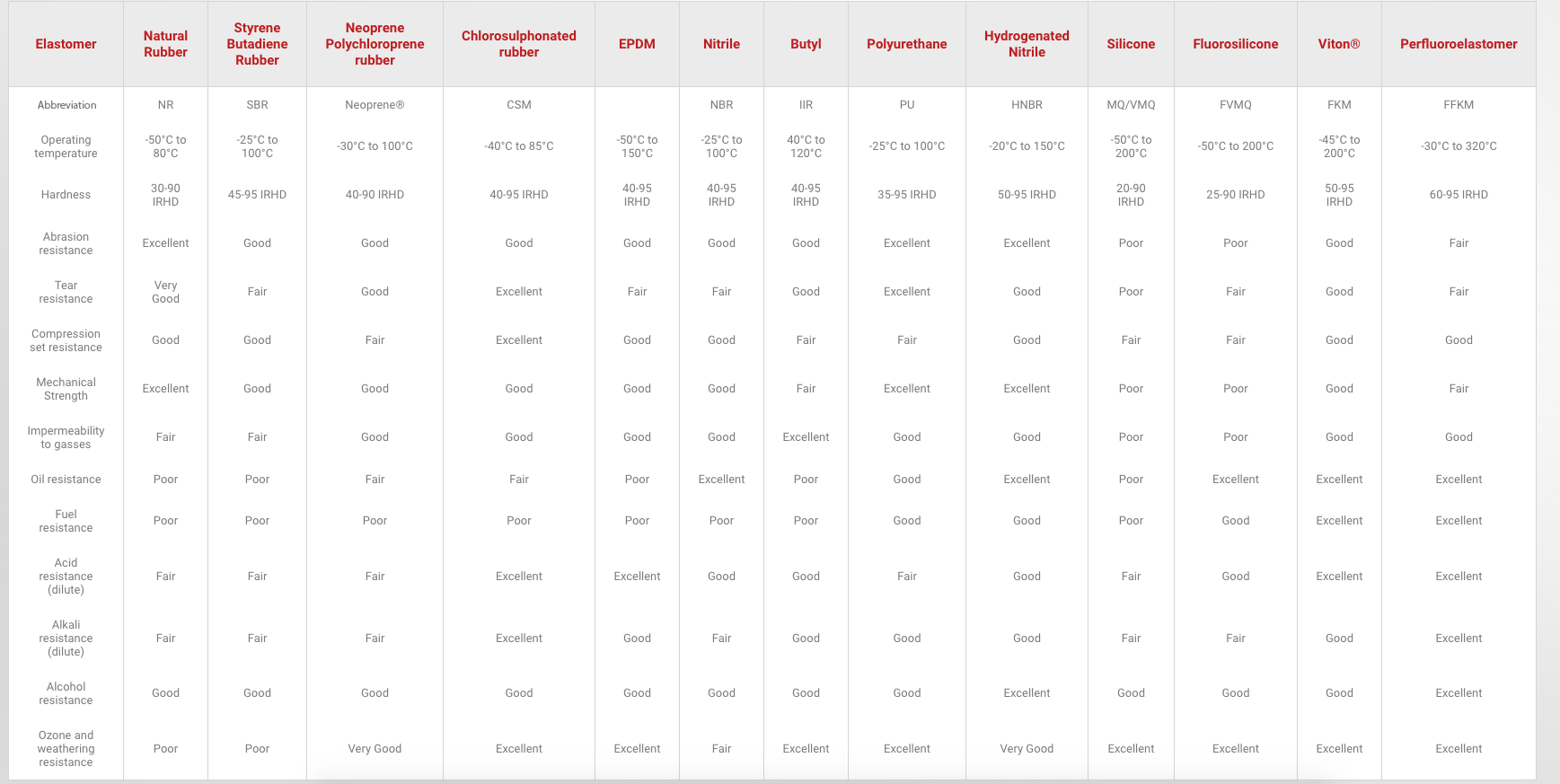
With so many different types of polymers available in today’s market, we appreciate that the selection process is not always straightforward. Which is why we have listed our full range of polymeric materials, and their full specifications below, to give you detailed overview of their characteristics. Here, you can find out the operating temperatures, hardness range, advantages, disadvantages and typical uses of each of our polymer materials.
Click on any of the polymers below to see further details on each one.
- Tetrafluoroethylene/propylene dipolymer (Aflas®)
ISO 1629 FEPM Operating Temperature -5°C to +200°C Hardness Range 70 to 90 IRHD Advantages
Excellent high temperature properties
Excellent resistance to acids and bases
Excellent steam resistance
Excellent resistance to sour gas (H₂S)
Good oil resistanceDisadvantages
Poor low temperature resistance
Poor compression set resistance
Poor extrusion resistance at high temperaturesTypical Use
Seal, 'O' rings and packers for oil and gas applications, gaskets for chlorine and chlorate manufacture
- Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR)
ISO 1629 SBR Operating Temperature -25°C to +90°C Hardness Range 40 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Excellent abrasion resistance
Good compression set resistance
Good water resistanceDisadvantages
Poor ozone and sunlight resistance
Poor steam resistance
Poor oil resistanceTypical Use
Rollers and feed tyres
- Silicone
ISO 1629 MQ / VMQ Operating Temperature -60°C to +250°C Hardness Range 20 to 90 IRHD Advantages
Excellent high and low temperature properties
Good flame resistance
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistanceDisadvantages
Poor tear strength & abrasion resistance
High gas permeability
Poor resistance to oils and non polar solventsTypical Use
Medical applications, seals for food applications, electrical insulation
- PTFE / Elastomer composites
ISO 1629 PTFE Operating Temperature -30°C to +200°C (depending upon elastomer core) Hardness Range 70 to 85 IRHD Advantages
Excellent chemical resistance
Easy of cleaning
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistance
Low friction
Cost effectiveDisadvantages
Some limitation on seal profiles
Higher sealing force required than standard elastomer sealsTypical Use
Chemical processing equipment, valves, chemical transport, pump diaphragms
- Polyurethane
ISO 1629 AU / EU Operating Temperature -35°C to +80°C Hardness Range 35 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Excellent tear and abrasion resistance
Good resistance to oils
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistance
Good low temperature propertiesDisadvantages
Poor steam resistance
Poor acid resistanceTypical Use
Products requiring good weather resistance, flame retardant products
- Polychloroprene rubber (Neoprene®)
ISO 1629 CR Operating Temperature -30°C to +100°C Hardness Range 40 to 90 IRHD Advantages
Good oil resistance
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistance
Good tear and abrasion resistance
Good flame resistance
Good acid resistanceDisadvantages
Poor resistance to compression set
Poor steam resistance
Poor fuel resistanceTypical Use
Products requiring good weather resistance, seals for refrigeration
- Perfluoroelastomer (FFKM)
ISO 1629 FFKM Operating Temperature -30°C to +330°C Hardness Range 65 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Excellent high temperature properties
Excellent chemical resistance
Excellent oil resistance
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistanceDisadvantages
Some grades have poor low temperature properties
Material costTypical Use
Chemical processing equipment, valves, aerospace, motorsport & semiconductor applications
- Nitrile
ISO 1629 NBR Operating Temperature -25°C to +100°C Hardness Range 40 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Good resistance to oils and non-polar solvents
Good resistance to compression set
Good abrasion resistance
Good resistance to acidsDisadvantages
Poor ozone and sunlight resistance
Poor steam resistanceTypical Use
Oil resistant automotive, marine and aerospace applications. Rollers
- Natural rubber
ISO 1629 NR Operating Temperature -45°C to +75°C Hardness Range 30 to 90 IRHD Advantages
Excellent resistance to abrasion & resilience properties
High tear strength & good compression set resistance
Very good low temperature properties
Strong bonding to metalDisadvantages
Poor oil resistance
Poor ozone and sunlight resistance
Poor resistance to steamTypical Use
Food seals, rubber to metal bonded items, rollers
- Hydrogenated Nitrile
ISO 1629 HNBR Operating Temperature -25°C to +150°C Hardness Range 50 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Excellent abrasion resistance
Good resistance to oils
Good ozone and sunlight resistance
Good resistance to fuelsDisadvantages
Reduced low temperature performance compared to standard nitrile
Poor steam resistanceTypical Use
'O' rings for oil & gas applications, packers, water stop seals
- Fluorosilicone
ISO 1629 FVMQ Operating Temperature -60°C to +200°C Hardness Range 25 to 90 IRHD Advantages
Good high temperature properties
Excellent low temperature properties
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistance
Excellent oil resistanceDisadvantages
Poor tensile strength & abrasion resistance
High gas permeabilityTypical Use
Medical applications, seals for aviation fuels
- Fluoroelastomer (Very low temperature)
ISO 1629 FKM Operating Temperature -40°C to +200°C Hardness Range 60 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Good high & low temperature properties
Good resistance to acids and bases
Excellent oil resistance
Good methanol resistance
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistanceDisadvantages
Lower chemical resistance than other high fluorine FKM grades
More expensive than other FKM gradesTypical Use
Seals, gaskets & 'O' rings for chemical processing, oil & fuel applications where low temperature operation is a critical requirement
- Fluoroelastomer (Type III)
ISO 1629 FKM Operating Temperature -25°C to +200°C Hardness Range 60 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Good high temperature properties
Improved low temperature properties
Excellent oil resistance
Good steam resistance
Good methanol resistance
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistanceDisadvantages
More expensive than other FKM grades
Typical Use
Seals, gaskets & 'O' rings for chemical processing, oil & fuel applications
- Fluoroelastomer (Type II)
ISO 1629 FKM Operating Temperature -10°C to +200°C Hardness Range 50 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Good high temperature properties
Excellent oil resistance
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistanceDisadvantages
Poor low temperature properties
Poor steam resistance
Limited methanol resistanceTypical Use
Seals, gaskets & 'O' rings for chemical processing, oil & fuel applications
- Fluoroelastomer (Type I)
ISO 1629 FKM Operating Temperature -10°C to +200°C Hardness Range 50 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Good high temperature properties
Excellent oil resistance
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistanceDisadvantages
Poor low temperature properties
Poor steam resistance
Poor methanol resistanceTypical Use
General purpose seals for automotive & aerospace fuel applications
- EPDM
ISO 1629 EPDM Operating Temperature -50°C to +150°C Hardness Range 40 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistance
Good resistance to compression set
Excellent tear and abrasion resistance
Excellent steam resistance
Good resistance to acidsDisadvantages
Poor resistance to oils and non-polar solvents
Poor fuel resistanceTypical Use
'O' rings, automotive cooling systems, window & glove box seals for nuclear applications, products required good weather resistance
- Chlorosulphonated rubber (CSM)
ISO 1629 CSM Operating Temperature -40°C to +85°C Hardness Range 40 to 95 IRHD Advantages
Excellent ozone and sunlight resistance
Good resistance to oils
Good resistance to acids
Good abrasion resistanceDisadvantages
Poor resistance to fuels
Poor steam resistanceTypical Use
Products required good weather resistance, flame retardant products, rollers
- Butyl
ISO 1629 IIR Operating Temperature -40°C to +120°C Hardness Range 40 to 90 IRHD Advantages
Low gas permeation
Excellent water resistance
Good resistance to acids
Good resistance to bases
Good damping properties
Good weather & sunlight resistanceDisadvantages
Poor oil resistance
Poor fuel resistanceTypical Use
Inner tubes for tyres, bladders and protective
For further information about what to consider when choosing types of polymers, please refer to our handy polymer selection FAQs. Read here to learn more about EPDM polymers, Neoprene polymer, Nitrile rubber and Styrene-Butadiene rubber.
Discuss your requirements with our engineers
Sometimes it's easier to just talk, contact us directly
Find out more about a specific product
Who we've worked with