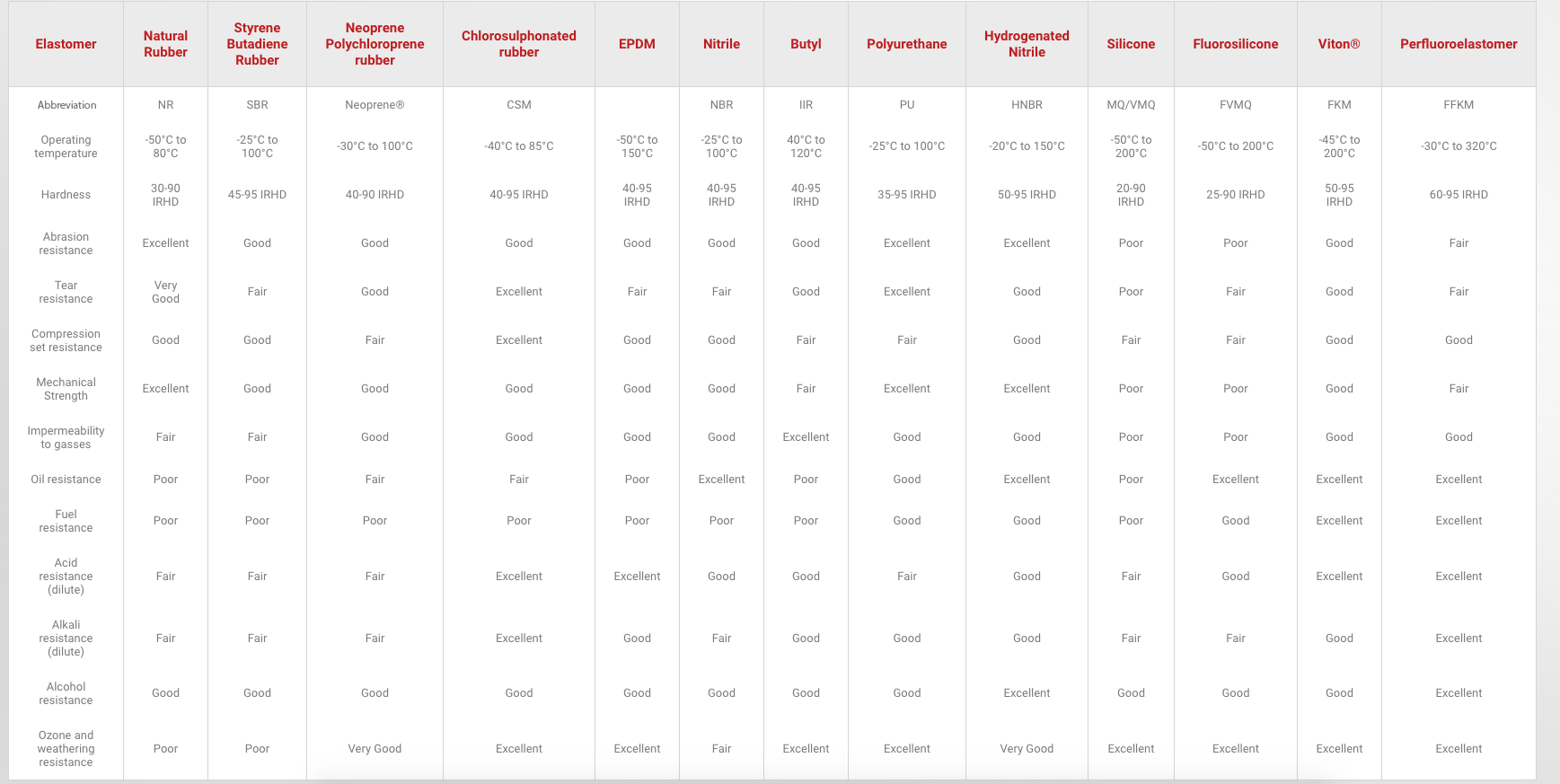
What are the different types of polymers and their properties?
When choosing a polymer material for your requirements, our expert polymerists at TRP Polymer Solutions weigh up a number of factors. These include the polymer’s hardness, tensile strength, elongation at break, compression set, specific colours and – crucially – the specific application environment your polymer material is likely to be exposed to on a day-to-day basis.
Every polymer has its idiosyncratic strengths and weaknesses, some more so than others, which makes material selection a crucial part of the product design process. Here, we outline the properties of just some of the different types of polymers we work with at TRP Polymer Solutions. Read on to find out more.
Different types of polymer and their properties
As you might expect from an experienced customer rubber moulding manufacturer, we work with a wide range of polymer materials through the course of our work. Which makes us ideally placed to explain the features and benefits of some of the most common polymers used in the industry. Let’s take a look at a few examples.
Butyl
Butyl rubber, also known as isobutylene-isoprene rubber or IIR for short, is a synthetic rubber that is made by copolymerising isobutylene with small amounts of isoprene. This synthetic rubber offers excellent water resistance and damping properties, as well as good resistance to acids, bases, weather and sunlight. Butyl also boasts low permeability to gas and moisture, which is why it is the material of choice for tyre inner tubes and bladders.
Chlorosulphonated rubber (CSM)
Chlorosulphonated Polyethylene, which also goes by the name of CSM and the DuPont brand name Hypalon, is a superior form of chloroprene (Neoprene). CSM offers excellent ozone and sunlight resistance, as well as good resistance to oils, acids and abrasion. Our CSM grades have operating temperatures of -40°C to +85°C, making them ideal for environments that are routinely exposed to extreme weather conditions and flames.
EPDM
EPDM, or Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer to give it its full name, is a copolymer of ethylene, propylene and a small amount of non-conjugated diene monomers that provide cross-linking sites for vulcanisation. This durable synthetic rubber offers a more cost-effective alternative to silicone where heat resistance is less of a priority. It also boasts excellent resistance to ozone, sunlight, compression set, tearing, abrasion, steam and acids.
Fluoroelastomers (FKM)
FKM is the ASTM designation for a class of fluorinated, carbon-based synthetic rubbers, known as fluoroelastomers. FKM offers impressive heat resistance in operating temperatures well in excess of +200 °C (+392 °F). FKM also offers excellent resistance to high pressures, chemicals and other fluids – including a number of fuels. Originally developed for the aerospace industry, FKM is now widely used across many industry applications.
Hydrogenated Nitrile
Hydrogenated Nitrile or HNBR is made by saturating nitrile with hydrogen on its hydrocarbon chains to produce a stronger, more resistant material. HNBR delivers excellent mechanical properties, even at higher temperatures and is resistant to steam and hot air. Our HNBR compounds are capable of operating in temperatures of -40 °C and +150 °C with a hardness in the range of 50 to 95 IRHD.
Nitrile
Nitrile rubber, also known as NBR, nitrile-butadiene rubber or Buna-N, is derived from acrylonitrile and butadiene. This synthetic rubber has a hardness in the range of 40 to 95 IRHD and performs well in operating temperatures of between -25 °C to +100 °C. Some of the standout features of nitrile include its good resistance to oils, non-polar solvents, compression set, abrasion and some acids. It is a common material for gaskets, seals and ‘O’ rings.
Perfluoroelastomers (FFKM)
FFKM, which comes under the umbrella of perfluoroelastomers, is a high-grade polymer material that boasts a highly fluorinated chemical composition, which makes it extremely resistant to chemicals, high temperatures and oxygen-plasma. FFKM combines the elasticity of FKM with the chemical resistance of PTFE. It also delivers excellent resistance to gas and liquid permeation, exceptional sealing performance and good mechanical properties.
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR)
Styrene-butadiene rubber or SBR is a general-purpose synthetic rubber made from a copolymer of styrene and butadiene. SBR is perhaps best-known for its use in car tyres and as an abrasion-resistant alternative to natural rubber. SBR has a wide range of beneficial properties, including excellent resistance to water, abrasion and compression set. Typical applications of styrene-butadiene rubber include rollers and feed tyres.
Contact TRP Polymer Solutions today
TRP Polymer Solutions offers all of these polymers and more. All of which are specially formulated to meet your specific application requirements. To find out more about our high-quality polymer products and manufacturing processes, or to discuss your requirements in more detail, please contact TRP Polymer Solutions today on +44(0)1432 268899 or email sales@trp.co.uk.